This post and all others for this month are part of the series which I used to help me prepare for my GIAC Reverse Engineer Malware (GREM) certification.
This post, I am looking at performing static analysis of the Brbbot malware. What do I hope to learn throughout the static analysis process about this malware? Anything that might suggest this program might be malicious. However, here are some of the things I have in mind:
- Get the file hash
- Whether the program is potentially malicious
- Whether or not the executable is packed
- Any type of obfuscation
- Interesting Strings
- Information on the functions imported
- Information on any functions which may be exported
- Information on the various sections within the executable
- Whether or not cryptography is involved
- Any information on digital certificates, etc., being used
The BrbBot executable was designed for Windows. However, to reduce the risk of accidentally compromising a system, you can run your analysis on a different operating system. In this case, I am performing my static analysis on both a Windows 10 VM and my Kali system.
Lets get going.
- Get the file hash
I will look at the hash from the MD5 perspective, using md5sum on my Kali system.
1 2 | └─$ md5sum brbbot.exe 1c7243c8f3586b799a5f9a2e4200aa92 brbbot.exe |
- Whether the program is potentially malicious
To answer this question, let's look at it from three different perspectives. First, we start with ClamAV
└─$ clamscan --verbose brbbot.exe Scanning brbbot.exe brbbot.exe: OK ----------- SCAN SUMMARY ----------- Known viruses: 8933105 Engine version: 0.103.0 Scanned directories: 0 Scanned files: 1 Infected files: 0 Data scanned: 0.07 MB Data read: 0.07 MB (ratio 1.00:1) Time: 18.415 sec (0 m 18 s) Start Date: 2020:11:07 21:32:42 End Date: 2020:11:07 21:33:01
Hmmm! Interesting that ClamAV did not find anything malicious here. Let's use Team Cymru Malware Hash Registry to query the hash which was returned from md5sum.
└─$ md5sum brbbot.exe | cut --fields 1 --delimiter " " | awk '{ system("whois --host hash.cymru.com "$1); }' | awk --field-separator " " '{ print $1 ; system("date --date=@"$2); print $3}' 1c7243c8f3586b799a5f9a2e4200aa92 Sat 07 Nov 2020 09:42:16 PM EST NO_DATA
└─$ wine ~/SysInternals/sigcheck64.exe -a -h -u -v brbbot.exe 1 ⨯ Sigcheck v2.80 - File version and signature viewer Copyright (C) 2004-2020 Mark Russinovich Sysinternals - www.sysinternals.com brbbot.exe: Verified: Unsigned Link date: 1:12 AM 2/25/2015 Publisher: n/a Company: n/a Description: n/a Product: n/a Prod version: n/a File version: n/a MachineType: 64-bit Binary Version: n/a Original Name: n/a Internal Name: n/a Copyright: n/a Comments: n/a Entropy: 5.918 MD5: 1C7243C8F3586B799A5F9A2E4200AA92 SHA1: 4DB5A8E237937B6D7B435A8506B8584121A7E9E3 PESHA1: 4DB5A8E237937B6D7B435A8506B8584121A7E9E3 PE256: n/a SHA256: F47060D0F7DE5EE651878EB18DD2D24B5003BDB03EF4F49879F448F05034A21E IMP: 475B069FEC5E5868CAEB7D4D89236C89 VT detection: 52/73 VT link: https://www.virustotal.com/gui/file/f47060d0f7de5ee651878eb18dd2d24b5003bdb03ef4f49879f448f05034a21e/detection
- Whether or not the executable is packed
To validate whether or not the file is packed. I first run strings on the file.
└─$ strings brbbot.exe | head --lines 10 !This program cannot be run in DOS mode. Rich .text `.rdata @.data .pdata @.rsrc @.reloc WATAUH \$@H
└─$ strings --all --encoding=s --bytes=10 brbbot.exe | more ... GetUserObjectInformationW GetLastActivePopup GetActiveWindow MessageBoxW brbconfig.tmp %s?i=%s&c=%s&p=%s Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 8.0; Windows NT 6.1; Trident/4.0) Connection: close ZwQuerySystemInformation RegSetValueExA RegOpenKeyExA RegDeleteValueA RegFlushKey RegCloseKey CryptAcquireContextW CryptDeriveKey CryptReleaseContext CryptEncrypt CryptCreateHash CryptDestroyKey CryptDecrypt CryptDestroyHash ...
- Any type of obfuscation
└─$ strings --all --encoding=s --bytes=10 brbbot.exe | more ... GetUserObjectInformationW GetLastActivePopup GetActiveWindow MessageBoxW brbconfig.tmp %s?i=%s&c=%s&p=%s Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 8.0; Windows NT 6.1; Trident/4.0) Connection: close ZwQuerySystemInformation RegSetValueExA RegOpenKeyExA RegDeleteValueA RegFlushKey RegCloseKey CryptAcquireContextW CryptDeriveKey CryptReleaseContext CryptEncrypt CryptCreateHash CryptDestroyKey CryptDecrypt CryptDestroyHash ...
Above, I conclude that the data is not obfuscated. More importantly, I am able to also identify interesting strings, information on the functions used by the program, functions which suggest cryptography is in use.
└─$ peframe brbbot.exe -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- File Information (time: 0:00:00.834525) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- filename brbbot.exe filetype PE32+ executable (GUI) x86-64, for MS Windows filesize 75776 hash sha256 f47060d0f7de5ee651878eb18dd2d24b5003bdb03ef4f49879f448f05034a21e virustotal / imagebase 0x140000000 * entrypoint 0x3f94 imphash 475b069fec5e5868caeb7d4d89236c89 datetime 2015-02-25 06:12:18 dll False directories import, tls, resources, relocations sections .rdata, .data, .pdata, .rsrc, .reloc, .text * features mutex, antidbg, packer, crypto -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Yara Plugins -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- IsPE64 IsWindowsGUI HasRichSignature Advapi Hash API -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Behavior -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- anti dbg Xor network http screenshot win registry win files operation -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Crypto -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Advapi Hash API -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Packer -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Microsoft Visual Cpp 80 DLL -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Mutex Api -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- WaitForSingleObject -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Anti Debug -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- GetLastError IsDebuggerPresent TerminateProcess UnhandledExceptionFilter -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Sections Suspicious -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- .text 6.34 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Import function -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ADVAPI32.dll 14 WININET.dll 9 WS2_32.dll 5 KERNEL32.dll 86 USER32.dll 1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Possibile Breakpoint -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- CloseHandle CopyFileA CreateFileA CreateFileW CreateProcessA CryptEncrypt DeleteCriticalSection DeleteFileA ExitProcess FindResourceA GetCommandLineW GetComputerNameA GetCurrentProcess GetCurrentProcessId GetFileSize GetModuleFileNameA GetModuleFileNameW GetModuleHandleA GetModuleHandleW GetProcAddress GetStartupInfoW GetSystemDirectoryA GetTempFileNameA GetTempPathA GetTickCount HeapAlloc HttpQueryInfoA HttpSendRequestA InitializeCriticalSectionAndSpinCount InternetCloseHandle InternetConnectA InternetOpenA InternetQueryDataAvailable InternetReadFile IsDebuggerPresent LoadLibraryW LockResource ReadFile RegCloseKey RegDeleteValueA RegOpenKeyExA SetFilePointer Sleep TerminateProcess UnhandledExceptionFilter WSAStartup WaitForSingleObject WriteFile -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- File -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- brbconfig.tmp Temporary ntdll.dll Library ADVAPI32.dll Library WININET.dll Library WS2_32.dll Library KERNEL32.dll Library USER32.dll Library
└─$ wrestool --list brbbot.exe --type='CONFIG' --name=101 --language=1033 [offset=0x17070 size=73]
└─$ sudo wrestool --extract --raw --verbose --out . brbbot.exe └─$ ls brbbot.exe* brbbot.exe brbbot.exe_CONFIG_101 └─$ file brbbot.exe_CONFIG_101 brbbot.exe_CONFIG_101: COM executable for DOS
└─$ exiftool brbbot.exe ExifTool Version Number : 12.09 File Name : brbbot.exe Directory : . File Size : 74 kB File Modification Date/Time : 2015:02:25 02:12:18-05:00 File Access Date/Time : 2020:11:07 21:14:58-05:00 File Inode Change Date/Time : 2020:11:07 21:12:42-05:00 File Permissions : rw-r--r-- File Type : Win64 EXE File Type Extension : exe MIME Type : application/octet-stream Machine Type : AMD AMD64 Time Stamp : 2015:02:25 01:12:18-05:00 Image File Characteristics : Executable, Large address aware PE Type : PE32+ Linker Version : 10.0 Code Size : 50176 Initialized Data Size : 35328 Uninitialized Data Size : 0 Entry Point : 0x3f94 OS Version : 5.2 Image Version : 0.0 Subsystem Version : 5.2 Subsystem : Windows GUI
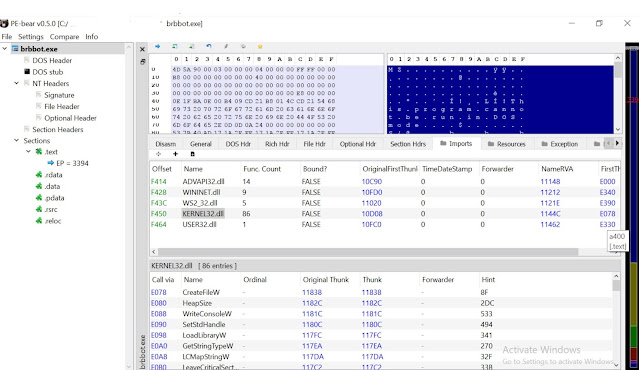
Similarly, there are tools such as PE-bear ...
... Detect It Easy
... and a whole host of other tools and techniques which can be used to gain additional insights via static analysis.
References:
Mastering 4 Stages Of Malware Analysis
CrowdStrike - What is Malware Analysis
Infosec Institute - Static Malware Analysis
Mandiant - Practical Malware Analysis
Medium - Malware Analysis 101
Understanding PE Structure, The Layman’s Way – Malware Analysis Part 2
Analysis of portable executable files with PEFRAME
PEFrame
Team Cymru - Malware Hash Registry
SANS FOR610 - Reverse Engineering Malware - GREM


No comments:
Post a Comment